Quantitative Easing Defined: Primary Speaking FactorsWith rates of interest close to zero, the Federal Reserve ventured one other
Quantitative Easing Defined: Primary Speaking Factors
- With rates of interest close to zero, the Federal Reserve ventured one other coverage instrument in quantitative easing
- After years of QE, the Financial institution of Japan has skilled diminishing financial and monetary returns
- Equally, the ECB has engaged in long-term refinancing operations (LTROs) as a type of quantitative easing, however their effectiveness stays in query
How Does Quantitative Easing Work?
Quantitative easing (known as ‘QE’) is a financial coverage instrument sometimes utilized by central banks to stimulate their home financial system when extra conventional strategies are spent. The central financial institution buys securities – most continuously authorities bonds – from its member banks, successfully growing the provision of cash within the financial system.
With elevated provide, the price of cash is decreased which makes it cheaper for companies to borrow cash to make use of for enlargement. This has the same impact to the usual curiosity short-term rate of interest cuts that central banks make use of; however relying on what they buy, such efforts can decrease the price for considerably longer loans. That would extra immediately affect lending for houses, autos and small companies.
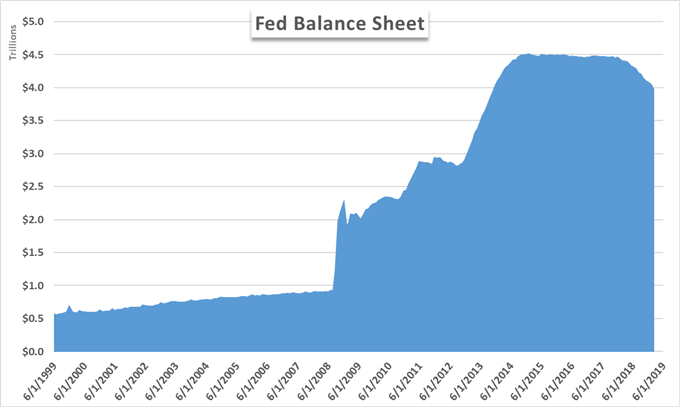
The Federal Reserve Financial institution (FED) Quantitative Easing Coverage
Because the central financial institution of the US, the Federal Reserve has an obligation to offer the nation…