Many merchants search for alternatives to commerce throughout risky market circumstances and whereas these durations supply nice
Many merchants search for alternatives to commerce throughout risky market circumstances and whereas these durations supply nice alternatives, the significance of timing can’t be ignored.
The intention of this text is to offer merchants a greater understanding of the MACD crossover and to display how it may be utilized in Foreign currency trading.
The MACD Crossover: What’s it?
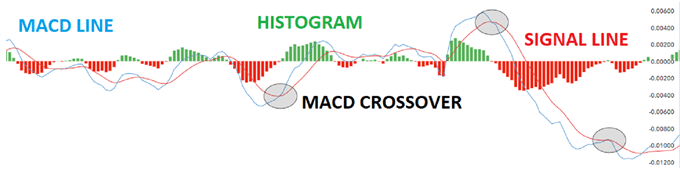
The Shifting Common Convergence/Divergence (MACD) is a technical indicator which makes use of the distinction between two exponential moving averages to find out the momentum and the course of the market. The MACD crossover happens when the MACD line and the sign line intercept, typically indicating a change within the momentum/development of the market. The MACD is seen as an effective indicator, particularly in trending markets.
Parts of the MACD:
- The MACD line: The MACD line (blue line) is the distinction between the 2 exponential transferring averages (normally the final 12 and 26 days or even weeks) and is normally known as the sooner line.
- Sign line: The sign line is normally a 9 interval exponentially smoothed common of the MACD line and might be known as the slower line.
- Zero line: The MACD traces fluctuate above and under a zero line, giving the MACD the qualities of an oscillator.
- Histogram: The histogram consists of vertical traces that present the unfold between the 2 MACD traces.