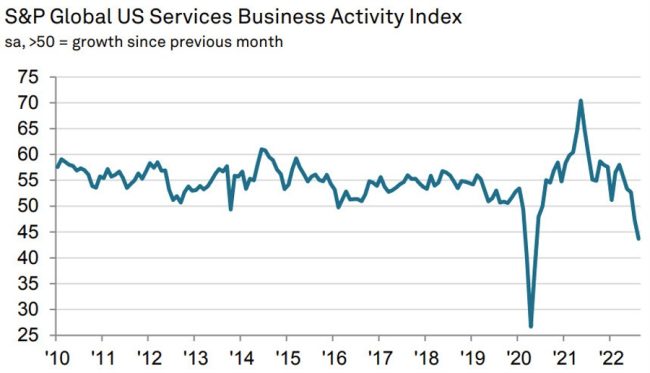
- Final services 43.7 vs 44.1 prelim and 47.3 prior
- Composite 44.6 vs 45.0 prelim and 47.7 prior
There’s a big divergence between this and the ISM services data, which is expected at 55.1 from 56.7 prior. To me, that highlights the risk of a big downside miss. If so, we could see some of today’s dollar strength unwound.
Chris Williamson, Chief Business Economist at S&P Global Market Intelligence, said:
“August saw the US economy slide into a steepening downturn, underscoring the rising risk of a deepening recession as households and business grapple with the rising cost of living and tightening financial conditions.
“Businesses are reporting a deterioration in output and order books of a degree exceeded since the global financial crisis only by that seen during the initial pandemic lockdowns.
“While orders are being lost across the board as a result of rising prices and the cost-of-living squeeze, the steepest downturn is being recorded in the financial services sector, reflecting the additional impact of higher interest rates and worsening financial conditions.
“Jobs growth has meanwhile cooled as companies grow increasingly reluctant to expand in the face of falling demand and an uncertain outlook, which will serve to further dampen growth in the coming months.
“One positive form the survey was a substantial fall in the rate of input cost inflation
Inflation
Inflation is defined as a quantitative measure of the rate in which the average price level of goods and services in an economy or country increases over a period of time. It is the rise in the general level of prices where a given currency effectively buys less than it did in prior periods.In terms of assessing the strength or currencies, and by extension foreign exchange, inflation or measures of it are extremely influential. Inflation stems from the overall creation of money. This money is measured by the level of the total money supply of a specific currency, for example the US dollar, which is constantly increasing. However, an increase in the money supply does not necessarily mean that there is inflation. What leads to inflation is a faster increase in the money supply in relation to the wealth produced (measured with GDP). As such, this generates pressure of demand on a supply that does not increase at the same rate. The consumer price index then increases, generating inflation.How Does Inflation Affect Forex?The level of inflation has a direct impact on the exchange rate between two currencies on several levels.This includes purchasing power parity, which attempts to compare different purchasing powers of each country according to the general price level. In doing so, this makes it possible to determine the country with the most expensive cost of living.The currency with the higher inflation rate consequently loses value and depreciates, while the currency with the lower inflation rate appreciates on the forex market.Interest rates are also impacted. Inflation rates that are too high push interest rates up, which has the effect of depreciating the currency on foreign exchange. Conversely, inflation that is too low (or deflation) pushes interest rates down, which has the effect of appreciating the currency on the forex market.
Inflation is defined as a quantitative measure of the rate in which the average price level of goods and services in an economy or country increases over a period of time. It is the rise in the general level of prices where a given currency effectively buys less than it did in prior periods.In terms of assessing the strength or currencies, and by extension foreign exchange, inflation or measures of it are extremely influential. Inflation stems from the overall creation of money. This money is measured by the level of the total money supply of a specific currency, for example the US dollar, which is constantly increasing. However, an increase in the money supply does not necessarily mean that there is inflation. What leads to inflation is a faster increase in the money supply in relation to the wealth produced (measured with GDP). As such, this generates pressure of demand on a supply that does not increase at the same rate. The consumer price index then increases, generating inflation.How Does Inflation Affect Forex?The level of inflation has a direct impact on the exchange rate between two currencies on several levels.This includes purchasing power parity, which attempts to compare different purchasing powers of each country according to the general price level. In doing so, this makes it possible to determine the country with the most expensive cost of living.The currency with the higher inflation rate consequently loses value and depreciates, while the currency with the lower inflation rate appreciates on the forex market.Interest rates are also impacted. Inflation rates that are too high push interest rates up, which has the effect of depreciating the currency on foreign exchange. Conversely, inflation that is too low (or deflation) pushes interest rates down, which has the effect of appreciating the currency on the forex market.
Read this Term, which should help to moderate consumer price growth in the months ahead, albeit with the rate of increase remaining stubbornly elevated.”
www.forexlive.com