All through historical past there have been plenty of extraordinarily significant volatility spikes throughout main monetary markets. Every had def
All through historical past there have been plenty of extraordinarily significant volatility spikes throughout main monetary markets. Every had defining traits that made them comparable, regardless of occurring in very completely different markets and for various causes.
The continuity seen throughout these volatility cycles is an effective factor, as a result of whereas it doesn’t essentially make a significant volatility spike predictable, historic priority provides a blueprint for figuring out situations which are supportive for a possible vol-event to happen, and the way they’re prone to unfold as soon as in movement. This may be of nice assist in guiding buying and selling choices, whether or not that’s to avoid a possible vol blow-up or transfer in direction of it with the suitable technique that may make the most of the outsized value swings that include uncommon ranges of volatility.
We’ll first focus on what a volatility occasion usually seems like when it comes to the conduct of volatility itself, then take a detailed have a look at a few of the largest spikes ever witnessed in main monetary markets.
What’s Volatility?
“In easy phrases, volatility will be outlined because the variations at which a market fluctuates. The extra an asset’s value strikes, the upper the volatility – the much less the value strikes, the decrease the volatility.”
– Paul Robinson, DailyFX
On this piece we’re a short-term measure of volatility (two-week period) known as Realized Volatility, which is volatility because it has already occurred. Additionally it is generally known as Historic Volatility.
What Does a Volatility Occasion Cycle Look Like?
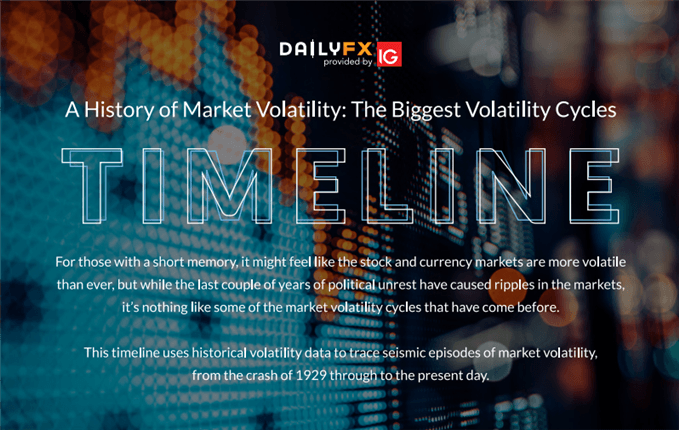
Within the lead-up to a volatility spike, there may be usually a build-up interval the place volatility rises steadily, indicating markets may very well be headed for important dislocation and disruption. The interval of delicate unrest is adopted by a sudden, vertical transfer in volatility that reaches a climax earlier than shortly reversing and normalizing by means of a gradual, however bumpy decline in direction of pre-event volatility ranges.
The graph beneath is a composite of a number of previous volatility cycles, accounting for 100 days earlier than and after the height in volatility. Discover the build-up interval, the volatility spike itself, and the normalization section, in addition to the asymmetry between the phases.
Cycle of a volatility spike
Supply: DailyFX
Conduct of Volatility Differs Amongst Asset Courses
One other facet of market volatility to grasp is that it doesn’t behave in the identical approach throughout all asset lessons, nor essentially even inside the identical asset class. For instance, inventory market volatility typically behaves in another way than it does in currencies and commodities.
Shares have had an inhelease lengthy bias to them, as they’re typically an asset of appreciating worth over the lengthyrun.
Market contributors spend money on firm shares, making the inventory market nearly an solely lengthy market with restricted quick curiosity. Due to this bias, volatility runs excessive in down markets when there may be worry because of monetary losses and promoting, and low in up markets the place worry is minimal.
Often, you will notice inventory market volatility rise in a bull market as contributors collectively undergo from FOMO, however this isn’t the norm and solely occurs in direction of the tip of lengthy, highly effective developments – a few which we are going to have a look at right here shortly.


Really helpful by Paul Robinson
Constructing Confidence in Buying and selling
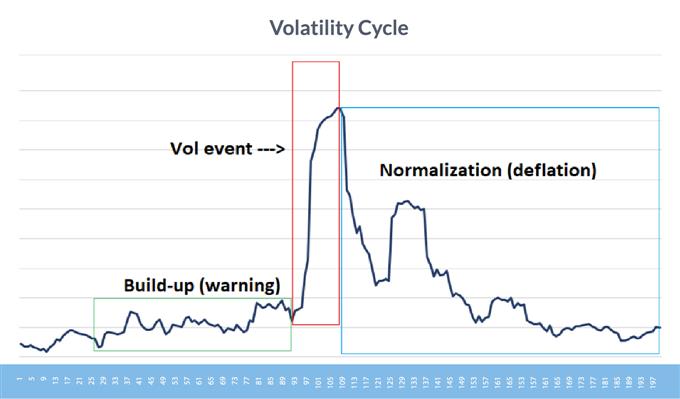
VIX demonstrates that volatility tends to rise on promoting, decline on shopping for
Knowledge Supply: Bloomberg
As proven within the graph above, volatility usually runs reverse of the S&P 500, particularly when the market declines.
Over the long-run, currencies and commodities don’t have a pure bias to them and have a tendency to oscillate in massive bull and bear cycles that finish in minimal web change. Volatility can rise in both course and isn’t constant over time. Within the case of commodities (i.e. gold), volatility can truly be extra prone to rise with a value rise than throughout a decline. However once more, this isn’t wholly constant throughout a cycle.
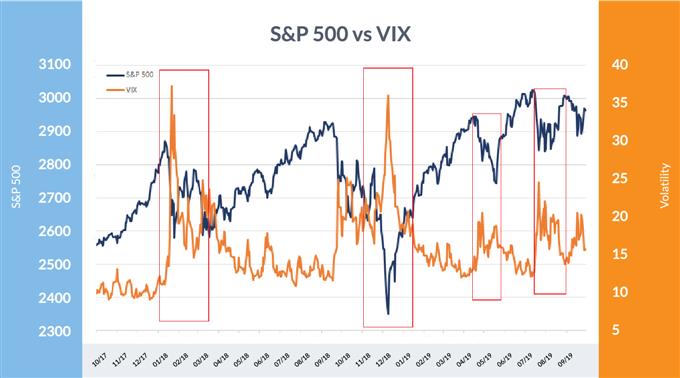
Gold vs two-week realized volatility
Knowledge Supply: Bloomberg
Within the graph above, the inexperienced containers mark intervals when volatility rose whereas value appreciated, and the purple containers mark intervals when it rose whereas the value of gold depreciated. This highlights the non-directional bias that volatility can have in commodities – the identical additionally holds true for forex volatility.
A Historical past of Market Volatility: The Largest Volatility Cycles
We’ll take a look on the a few of the most important volatility cycles which have occurred within the main monetary markets since 1929 and examine their build-up, peak, normalization section and after-effects.
Crash of 1929
On the finish of the roaring ‘20s’ bull market, the crash of 1929 kicked off the Nice Despair of the 1930s. The October 28-29 crash in 1929 is especially noteworthy and resulted in a two-day lack of 24% within the Dow Jones Industrials Common, with two-week realized volatility rocketing to 127%. Within the short-term aftermath, the Dow value spent the subsequent two weeks closing 6% greater or decrease from the prior day’s session.
As was the case with the loss of life of different main historic inventory markets, the crash didn’t come from all-time highs (ATH), however after a interval of weak point that brought about volatility to rise forward of the foremost spike. Heading into the late-October rout, the market was already off the ATH by 21% with short-term volatility rising from solely 11% to 81%.
After the preliminary episode of the 1929-1932 inventory market decline, volatility initially normalized by falling from a two-week studying of 127% to underneath 10% in about 5 months’ time. Volatility would ramp up once more later, however didn’t exceed 100% once more till nearly two years later, when the worst a part of the bear market drew close to its conclusion.
Dow Jones Industrial Common: 1929-1931
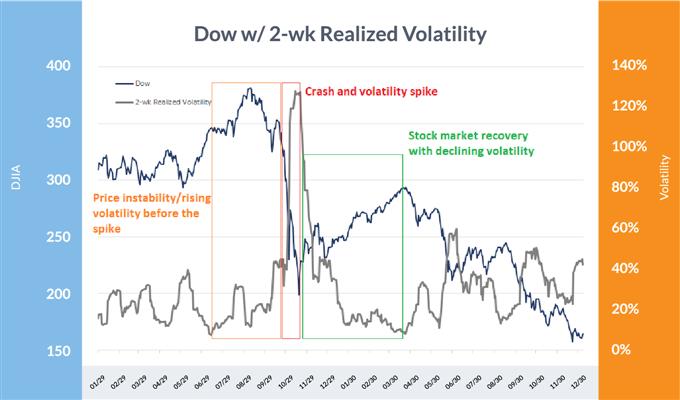
Knowledge Supply: Bloomberg
Within the chart above, volatility spiked sharply (purple) after weeks of rising in an unsteady market (orange), then dropped sharply (inexperienced) as market confidence firmed up within the wake of the two-day crash.
Silver 1980
Through the late 1970s/80s interval, the Hunt brothers tried to control the value of silver in what was probably the most well-known market ‘cornerings’ ever. It wasn’t simply the brothers’ buying and selling exercise although: inflation was quickly rising, and valuable metallic hedges have been in excessive demand. Silver topped out at over $49 after buying and selling at solely $6 a yr prior.
Through the spectacular value rise, volatility at occasions rose sharply with every main surge, together with the ultimate one which concluded in January 1980. Volatility declined in the course of the preliminary portion of the sell-off earlier than spiking to close document ranges because the market panicked out of lengthy positions in the course of the spring of 1980. From there it was a bumpy trip, however the two-week realized volatility declined to solely 12% a mere 5 months after super-spiking to 240%.
Silver: 1979-1981
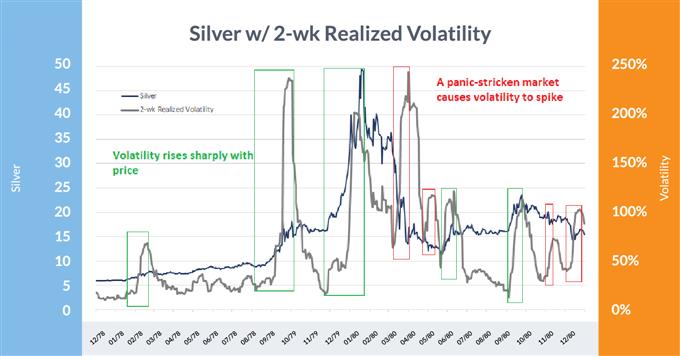
Knowledge Supply: Bloomberg
On this chart, the inexperienced containers spotlight the volatility spikes throughout bullish phases and the purple containers when volatility spiked on promoting. It’s clear there was a bigger tendency for volatility to rise with the value of silver versus when it fell.
Black Monday – 1987
The 1987 inventory market crash in america was largely blamed on ‘program buying and selling’, the primary know-how/monetary engineering-driven crash of its form. Nevertheless, huge speculative excesses have been constructed up previous to the crash, not like something because the 1920s.This performed a major function within the decline of inventory costs and the huge spike in volatility.
The one-day, 20%+ decline within the main averages was after all a major shock – exterior the opportunity of projection – however as has been the case with most different main volatility cycles, it didn’t precisely happen out of the blue.
Over the past ~10% of the bull market, two-week realized volatility rose with the S&P 500 from 8% to 15%, highlighting rising instability within the uptrend. By the point Black Monday rolled round, the SPX had already declined from the excessive by 16% whereas volatility was materially greater with a short-term studying of 25%.
Brief-term volatility spiked to over 130% within the wake of the Monday collapse in inventory costs earlier than easing off and finally dropping again to close 10% by the next March.


Really helpful by Paul Robinson
Get Your Free Prime Buying and selling Alternatives Forecast
S&P 500: 1987-88
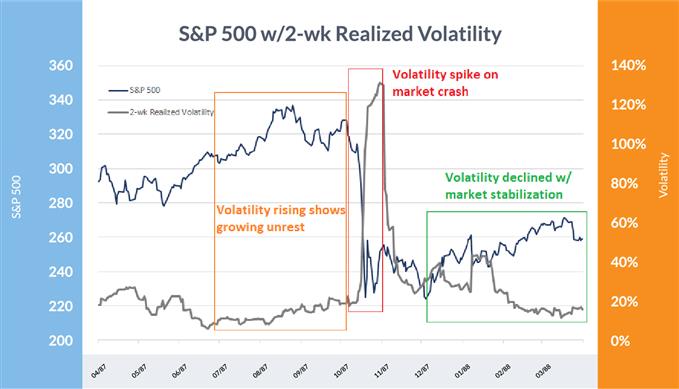
Knowledge Supply: Bloomberg
Rising unrest (orange) exhibits volatility growing because the market continues to be in a bullish section. When Black Monday rolled round, volatility went spiraling greater (purple) earlier than dropping off after the market stabilized (inexperienced).
Nice Monetary Disaster (GFC) 2008
The Nice Monetary Disaster was pushed by irresponsible banking practices on Wall St. that finally got here at the price of Fundamental St. The decline from 2007 to 2009 was the most important plunge in each shares and the financial system because the Nice Despair, nevertheless it wasn’t with out some kind of warning {that a} main blow-up in volatility may very well be within the works.
Simply earlier than issues received actually wild within the fall of 2008, two-week volatility was already at 41%. From there, the S&P 500 fell one other 27% in about 5 weeks, which noticed short-term volatility rocket to 97%. Throughout that point, the widely-watched VIX index exploded from 36 to 80. Within the yr following, volatility normalized with two-week realized vol and the VIX hitting 20% and 23, respectively.
However even going again to 2007 earlier than the bear market started, like in so many different bull markets nearing their conclusion, volatility started creeping greater. Regardless of the S&P 500 having gained about 8% YTD as much as the October 9, 2007 excessive, the VIX itself had additionally risen from round 12 to 16 – a 25% enhance. The wheels on the bus have been starting to wobble regardless of all trying effectively on the floor.
S&P 500: 2007-08

Knowledge Supply: Bloomberg
Trying on the chart above, one can see volatility was typically heading greater (orange) previous to the large spike in 2008. As soon as panic hit a zenith (purple) and market confidence got here again, volatility died down (inexperienced).
AUD/USD: 2008-09
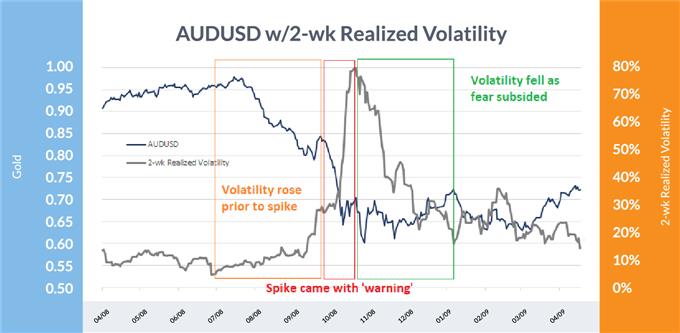
Knowledge Supply: Bloomberg
Turning to currencies, one of many largest casualties of the Nice Monetary Disaster was the Australian Greenback (AUD/USD), which plunged practically 40% as two-week volatility spiked to 80% from simply single digit ranges just a few months earlier. Australia’s robust export ties to China proved to be expensive when the rising financial system’s progress charge took a critical hit in the course of the world recession.
The rout wasn’t a complete shock, as few are; volatility rose steadily within the months previous to the ultimate collapse of Aussie. Brief-term volatility climbed from a mere 5% in July 2008 to almost 30% earlier than the ultimate spike to 80% occurred into October. As soon as AUD/USD bottomed there was a reasonably sharp drop in volatility earlier than it tapered off in the course of the first few months of 2009.
Different forex pairs have been additionally hit in a giant approach, similar to EUR/USD and USD/CAD, however volatility by no means escalated prefer it did in AUD/USD. Volatility in these pairs rose to ‘solely’ 30-40%, which continues to be extraordinarily excessive for currencies.
S&P 500 E-Mini Flash-Crash 2010
The primary main flash-crash to talk of occurred on Might 6, 2010, when the S&P 500 e-mini futures have been rocked by over 6% in about seven minutes earlier than erasing all losses in lower than fifteen minutes.
A London-based dealer, Navinder Singh Sarao, was accused and located responsible of ‘spoofing’ – the putting of enormous orders that are cancelled simply earlier than getting crammed.
Now whereas this may occasionally have contributed to the decline, the market was already in a fragile state to start with, as is usually the case when flash-crashes happen. To place volatility into perspective, the VIX had risen from 15 to 25 within the weeks prior, earlier than rocketing previous 40 on the day of the crash. Volatility truly didn’t end rising till about three weeks later when the VIX hit 48. From there, volatility declined in typical style till early 2011 earlier than popping once more.
S&P 500: 2010
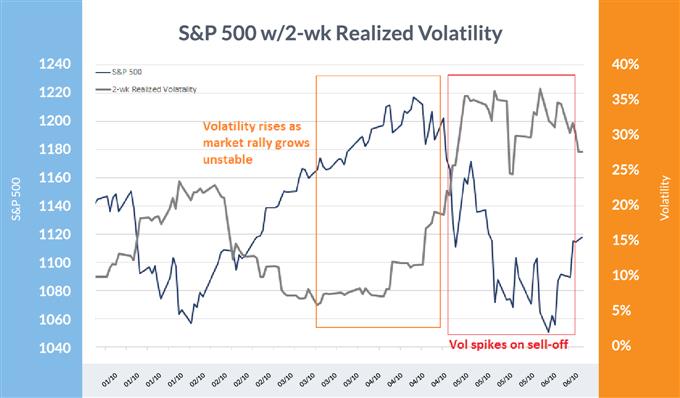
Knowledge Supply: Bloomberg
The S&P 500 e-mini flash-crash confirmed afamiliar theme: the orange field highlights a interval the place shares have been nonetheless typically heading greater however the unrest beneath the hood was changing into obvious by way of rising volatility. The spike and better ranges of volatility (purple) adopted swimsuit together with the Might 6 flash-crash.
EURCHF blow-up 2015
Of the blow-ups in volatility, this was one of many extra shocking. The Swiss Nationwide Financial institution (SNB) had a flooring within the EUR/CHF alternate charge that brought about wide-spread complacency out there and fueled the ‘pondering’ that the central financial institution would preserve the cross supported. Because it turned out, this was not the case.
When the SNB eliminated the ground, EUR/CHF collapsed from 1.20 – relying on the quote supply – to as little as 0.68. Brief-term volatility went from just about zero to almost 100% in a flash. It solely took days to take again a lot of the spike, however vol spent the subsequent three months slowly normalizing.
EUR/CHF: 2014-15
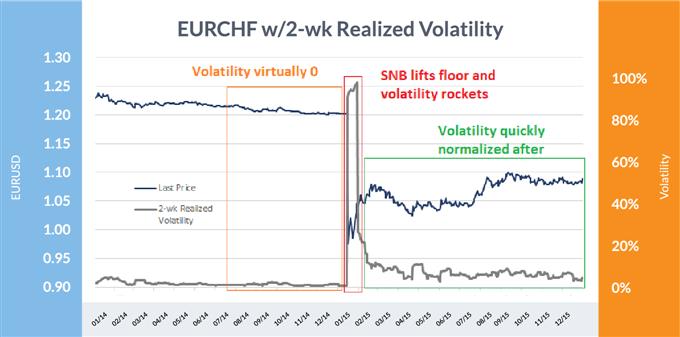
Knowledge Supply: Bloomberg
With the SNB flooring in place volatility dropped to almost zero (orange), however as soon as the ground was lifted the market was caught off guard, inflicting volatility to rocket to over 100% (purple) earlier than backing off as soon as the mud had settled (inexperienced).
Brexit 2016
The Brexit vote in June 2016 wasn’t anticipated, regardless of it being a chance, as evidenced by the best way markets have been hammered when the vote got here out in favor of the UK leaving the European Union. Sterling was in a near-term upswing proper earlier than the outcomes have been introduced, however GBP/USD ended up closing down 8% on the day that the vote was finalized. Two-week realized vol exceeded 46% thereafter.
This was a identified occasion to happen, so there was no shock to see volatility rise forward of time in anticipation – however, volatility offered a warning that issues might get dicey. Within the month earlier than the vote, two-week realized volatility rose from a mere 6% to over 16% as market contributors weighed in on the potential end result, one which the market wasn’t totally ready to deal with even with warning.
Submit-Brexit vote, volatility initially cratered from 46% again to 16% in solely a few month earlier than getting into the standard post-event grind in direction of normalization of round 7% in six weeks’ time. A number of months after that there was the Pound flash-crash in October that once more noticed volatility spiral greater momentarily.


Really helpful by Paul Robinson
Entry the newest GBP Forecast
GBP/USD & Vol Chart
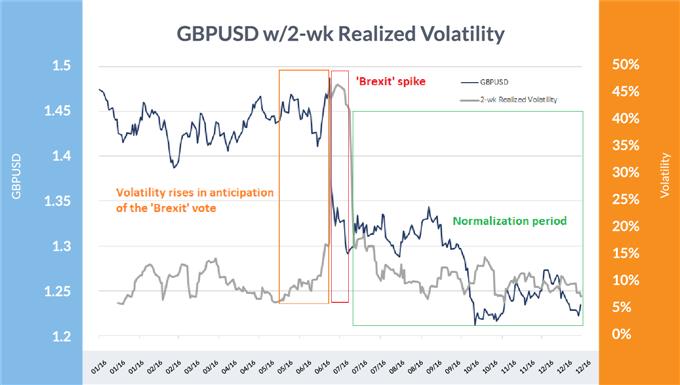
Knowledge Supply: Bloomberg
Above it may be seen that volatility rose in anticipation of the Brexit vote (orange), then rose sharply on the shock Brexit end result (purple) to finally fade within the aftermath (inexperienced).
Volpocalypse 2018
The ‘Volpocalypse’ of February 2018, whereas nowhere close to as dramatic and damaging because the ’87 crash, didn’t precisely occur out of the blue. Within the last months of 2017, U.S. shares accelerated greater in an unsustainable style, taking vol with it – two-week realized volatility rose from simply 3% on the finish of September to round 8% at its peak in January 2018.
After shares peaked in late January, the market started to say no for a few week earlier than the indices plunged and volatility shot up. The Dow skilled a 4% flash-crash within the span of about ten minutes.
The VIX, the preferred measure of broad inventory market volatility, noticed an especially uncommon spike because the market was caught betting closely on low ranges of volatility by way of futures, choices, and ETFs geared toward direct bets on the extent of the VIX. This brought about an exaggerated transfer within the VIX that pushed it to an intra-day excessive of 50. Like most vol blow-ups, this one too spent a number of months normalizing to pre-event ranges.
S&P 500 and VIX: 2018
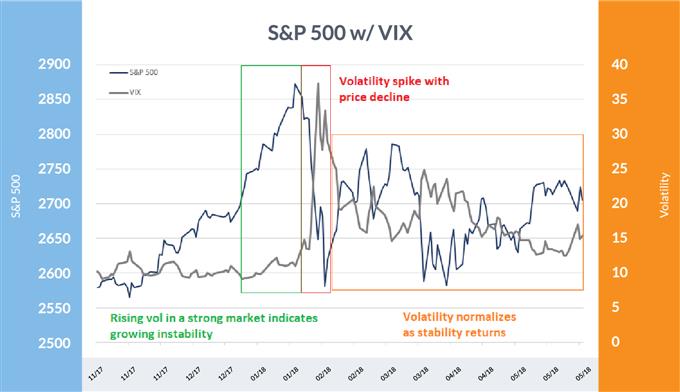
Knowledge Supply: Bloomberg
Above, you may see that volatility started rising over the past stage of the blow-off rally because it grew to become unstable (inexperienced) and rose additional on value weak point earlier than super-spiking on a pointy decline in inventory costs (purple), adopted by a interval of normalization (orange).
VIX Hits 50 intra-day
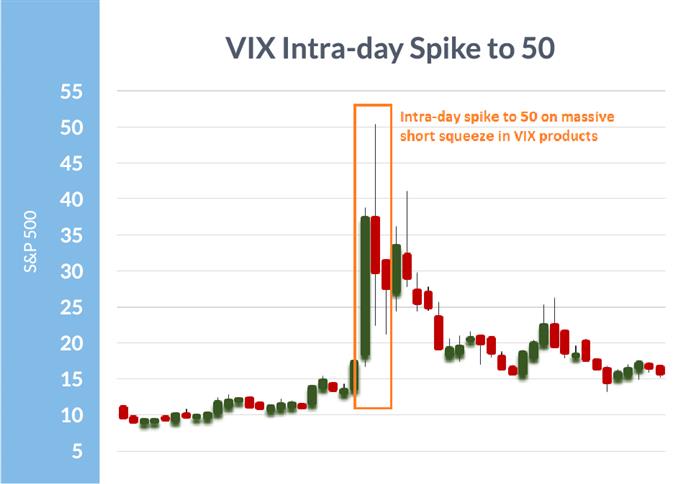
Knowledge Supply: Bloomberg
The intra-day VIX spike was a lot bigger than the precise inventory market decline would have brought about underneath ‘regular’ circumstances, however huge quick VIX bets helped gasoline it a lot greater.
Market Volatility Going Ahead
Main volatility occasions have at all times been part of monetary markets and at all times might be. Understanding what they seem like and having historic priority to function as blueprints provides merchants a framework to function inside going ahead.
Obtain the IG Consumer Sentiment Report to find whether or not our merchants are going lengthy or quick, how that is altering over time, and whether or not market indicators are bullish or bearish.
aspect contained in the
aspect. That is most likely not what you meant to do!nn Load your software’s JavaScript bundle contained in the aspect as an alternative.www.dailyfx.com
